
Acid and Base Balance
Metabolic Acidosis and Alkalosis:

7.35 - 7.45
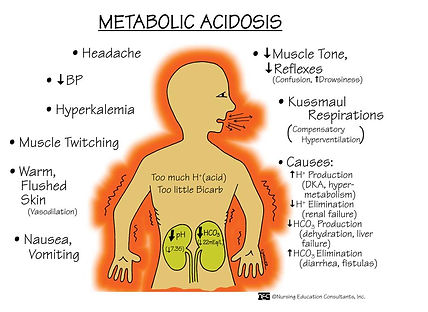
Metabolic Acidosis may occur due to:
A build up of acidic substances in the body or a loss of bicarbonate which is a crucial aspect of the pH buffer system.
When:
Can occur when the pH lowers creating a more acidic environment or when the kidney's can not expel appropriate amounts of acid to maintain a balance.
How:
-
Diarrhea- Loss of sodium bicarbonate through elimination
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis- When sugar levels are not maintained the body begins to utilize fat and muscle which creates ketones which are fatty acids- increasing the acidity within the body.
-
Renal Failure- Can not excrete enough acidic substance causing a buildup within the body.
Symptoms:
Headache, Lethargy, Nausea, Deep rapid breathing, Severe symptoms: Abdominal discomfort, abnormal heart beat (dysrythmias) and coma.
Diagnosis:
Testing the chemical levels of sodium, bicarbonate and chloride within blood.
Testing the arterial blood gases which determine the pH of the blood which is effected by levels of oxygen and hydrogen.
Testing the urine for presence of ketones which in turn increase the acid levels within the body.
pH less than 7.35 demonstrates acidosis.
Treatment:
Replace the imbalance through electrolyte and fluid replacement, Oxygen treatment and if necessary kidney treatment known as Dialysis.
Click the picture to see a bigger view
Metabolic Alkalosis may occur due to:
A loss of acidic substances within the body causing a build up of basic or alkaline substances typically loss of hydrogen, calcium, chloride and potassium.
When:
Can occur when the pH increases creating a basic or alkaline environment within the body.
How:
-
Loss of gastric acid secretions- due to stomach suctioning, or vomiting.
-
Kidney loss- Use of medications to stimulate urination or impaired kidney function.
-
Use of antacids such as Tums, Mylanta or Rolaids i.e
-
Use of laxatives or increased bowel elimination- rid body of natural potassium, chloride, calcium and sodium.
-
Alcohol abuse, or ingestion of bicarbonate ingredients such as in baking soda.
Symptoms:
Abnormal heart beat (dysrythmias), Weakness, muscle cramping, irregular movement of limbs (convulsions), confusion, hyper reactive reflexes
Severe symptoms: difficulty breathing, coma, dizziness, extreme confused state(stupor).
Diagnosis:
Testing the chemical levels of body as seen with metabolic acidosis. Urine test, Arterial blood gases, and blood tests.
pH greater than 7.45 demonstrates alkalosis.
Treatment:
Replace the imbalance through electrolyte and fluid replacement, Depending on the reason for alkalosis various treatments maybe used.

Click the picture to see a bigger view
References
Complimentary Medical Association (CMA). (n.d). Body pH balance. Photo retrieved from https://www.google.com/search? q=acid+base&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiMt4LRx9jPAhXMWh4KHTWYDJsQ_AUICCgB&biw=1366&bih=662#tbm=isch&q=body+ph+balance&imgrc=s9SS0xC07JTcJM%3A
Heuther, S. E., & McCance, K. L. (2017). Fluids and Electrolytes, Acids and Bases. In Understanding Pathophysiology. (Sixth ed., pp. 114-131). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier.
Nursing Education Consultants Incorporated (NECI). (2007). Metabolic alkalosis. Photo retrieved from https://www.google.com/search?q=acid+base&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiMt4LRx9jPAhXMWh4KHTWYDJsQ_AUICCgB&biw=1366&bih=662#tbm=isch&q=metabolic+acidosis+vs+alkalosis
Nursing Education Consultants Incorporated (NECI). (2007). Metabolic acidosis. Photo retrieved from https://www.google.com/search?q=acid+base&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiMt4LRx9jPAhXMWh4KHTWYDJsQ_AUICCgB&biw=1366&bih=662#tbm=isch&q=metabolic+acidosis+vs+alkalosis
TheVivianWho. (May 28th 2012). Video Retrieved from
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kzcAFtm-n0w
This tab was created on October 16, 2016
Last edited on October 23, 2016